Autologous Cell Therapy Development Platform
Autologous cell therapy is currently widely regarded as one of the most promising therapy approaches with the potential to cure various intractable diseases. As an innovative company specializing in the development of therapies for rare diseases, our company is dedicated to providing clients with autologous cell therapy development services.
Overview of Autologous Cell Therapy
Autologous cell therapy is an innovative therapeutic approach in which a person's own cells are used as therapeutic agents. This approach utilizes the natural healing and regenerative abilities of cells in order to repair diseased cells or rebuild functioning cells and tissues, minimizing the risk of rejection and adverse immune reactions.
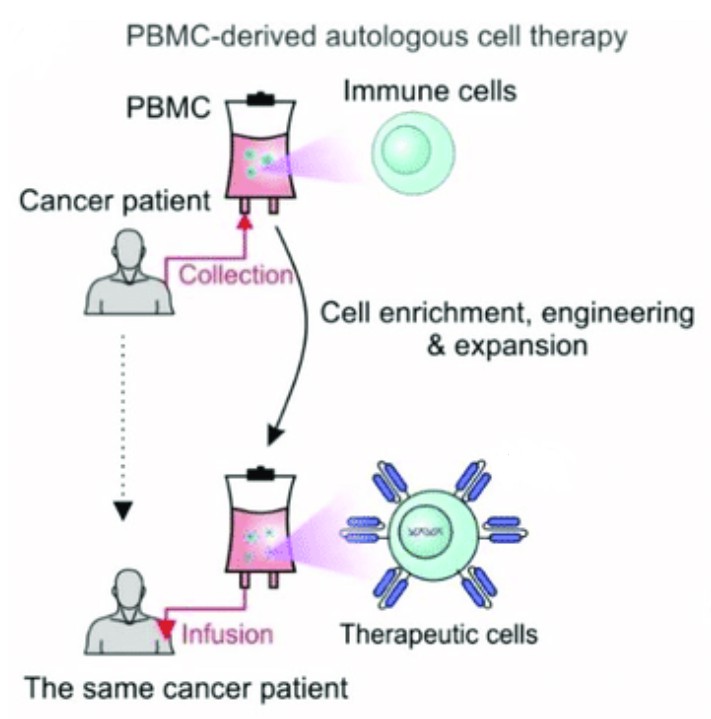 Fig. 1 BMC-derived autologous cell therapy (Yang Zhou, 2022)
Fig. 1 BMC-derived autologous cell therapy (Yang Zhou, 2022) Autologous Cell Therapy Versus Allogeneic Cell Therapy
| Autologous Cell Therapy | Allogeneic Cell Therapy | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Using patient's own modified immune cells to treat diseases | Using engineered/non-engineered cells from healthy donors to treat diseases |
| Cell Source | Cells from patient | Cells from healthy donor |
| Immunophenotyping | Strict immunophenotype match is not required | Matching is necessary to reduce rejection reaction |
| Advantages | Avoiding matching problems and risks, high safety | Powerful immune effects, extensive applicability, large-scale preparation |
| Disadvantages | Complexity and high cost,limited curative effect, limited scope of application | Risk of immune rejection, risk of infectious diseases, high cost, long period |
Autologous Cell Therapy Goal
- Assisting the immune system in recognizing and targeting specific cancer cells.
- Enhancing the immune cells to effectively eliminate cancer.
- Providing additional substances to bolster immune response.
Autologous Cell Therapy in Diseases
There are several autologous cell therapy methods that have been approved and successfully launched to the market. An increasing number of therapy methods are making significant breakthroughs in rare diseases pre-clinical studies. Currently, the primary categories of autologous cell therapy methods are as follows:
- Limb Ischemia
- Acute Radiation Disease
- Blood Disorders
- Autoimmune Diseases
- Acute Complete Spinal Cord Injury
- Malignant Diseases
- Fibrosis Diseases
- Ischemic Stroke
- Infectious Diseases
- Ocular Disorders
Our Services
Autologous cell therapy has shown promising results in preclinical research, but there are still many challenges and problems in the research process. By choosing our company for your allogeneic cell therapy development project, we can boost and optimize your research program with our comprehensive services which include:

Cell Services
- Acquisition and culture of multiple cells
- Differentiation and expansion of cells
- Modification and gene editing of cells
- Design and construction of molecular structure

Analysis Services
- Characterization of cells
- Cell antigen analysis
- Cell secretion and cytokine analysis
- Sanger sequencing and NGS analysis

Animal study Services
- Transgenic Mouse Model
- Human Xenograft Mouse Model
- Off-target Cellular Toxicity Mouse Model
Types of Autologous Cell Therapies
Stem Cells
- Bone Marrow Stem Cell Transplantation
- Peripheral Blood Stem Cell Transplantation
Immune Cells
- NK Cell Therapy
- DC Cell Therapy
- CAR-T Cell Therapy
- NK Cell Therapy
- CTL Cell Therapy
- TCR-T Cell Therapy
- CAR-M Cell Therapy
- CIK Cell Therapy
- LAK Cell Therapy
- TIL Cell Therapy
Autologous Cell Therapy Development Workflow

Why Choose Us
- Professional cell therapy strategies
- Extensive experience in preclinical research
- Competitive pricing and fast turnaround time
As a biotechnology company with substantial expertise in autologous cell therapy development for rare diseases, our company is here to provide our clients with effective, customized approaches through research. If you are interested in our autologous cell therapy development for rare diseases services, please contact us for more information.
Reference
- Harris DT, Kranz DM. Adoptive T Cell Therapies: A Comparison of T Cell Receptors and Chimeric Antigen Receptors. Trends Pharmakoi Sci, 2016, 37(3):220-230.
All of our services and products are intended for preclinical research use only and cannot be used to diagnose, treat or manage patients.
