The advent of antibiotics has had a positive impact in the field of medicine, particularly to the treatment of infections. At our company, we are equally involved in developing new antibiotics that stand to revolutionize the treatment of infectious diseases.
What are Antibiotics?
Antibiotics are chemicals used for the treatment of infections caused by bacteria that may either be artificially synthesized or extracted from biosynthetics. Antibiotics hold immense importance in medical science as they treat various bacterial infections. They have undoubtedly improved the overall health of people while averting potential greater challenges and saving lives.
 Fig. 1 Mechanisms of action of some antibiotics. (Aranda F L, Rivas B L., 2022)
Fig. 1 Mechanisms of action of some antibiotics. (Aranda F L, Rivas B L., 2022)
How Do Antibiotics Work?
Antibiotics eliminate bacteria by employing many methods that either disintegrate the bacteria's physical structure or the functional unit of its cell.
Destroying Bacterial Cell Walls
Bacterial cells are surrounded by cell walls that serve a double purpose – offering structural support while protecting the cell from outside damaging forces. Antibiotics attack a bacterium's cell wall by blocking the synthesis of the cell walls which results in rupture and removal of the bacterial cell.
Inhibiting Protein Synthesis
In bacterial cells, proteins perform many functions including enzyme function, structural function, and many cell functions. Antibiotics act upon the ribosomes in bacteria cells and inhibit their ability to synthesize proteins, thus inhibiting growth and survival.
Interfere with DNA Replication
The process of DNA replication enables the bacterial cell to duplicate and divide itself. Antibiotics acting on DNA replication impede an essential requirement, and this renders the bacterial cells incapable of division, hence, preventing the infection from spreading.
Approved Antibiotics as Infectious Disease Therapeutics
| Antibiotics |
Mechanism |
Indications |
| Amoxicillin |
Inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis |
Respiratory tract infections, urinary tract infections, and skin infections |
| Ceftriaxone |
Inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis |
Severe respiratory tract infections, meningitis, and sexually transmitted infections |
| Azithromycin |
Inhibit protein synthesis |
Respiratory tract infections, skin and soft tissue infections, and genitourinary tract infections |
| Levofloxacin |
Inhibit DNA replication |
Respiratory tract infections, urinary tract infections, and skin and soft tissue infections |
Challenges in Antibiotic Development
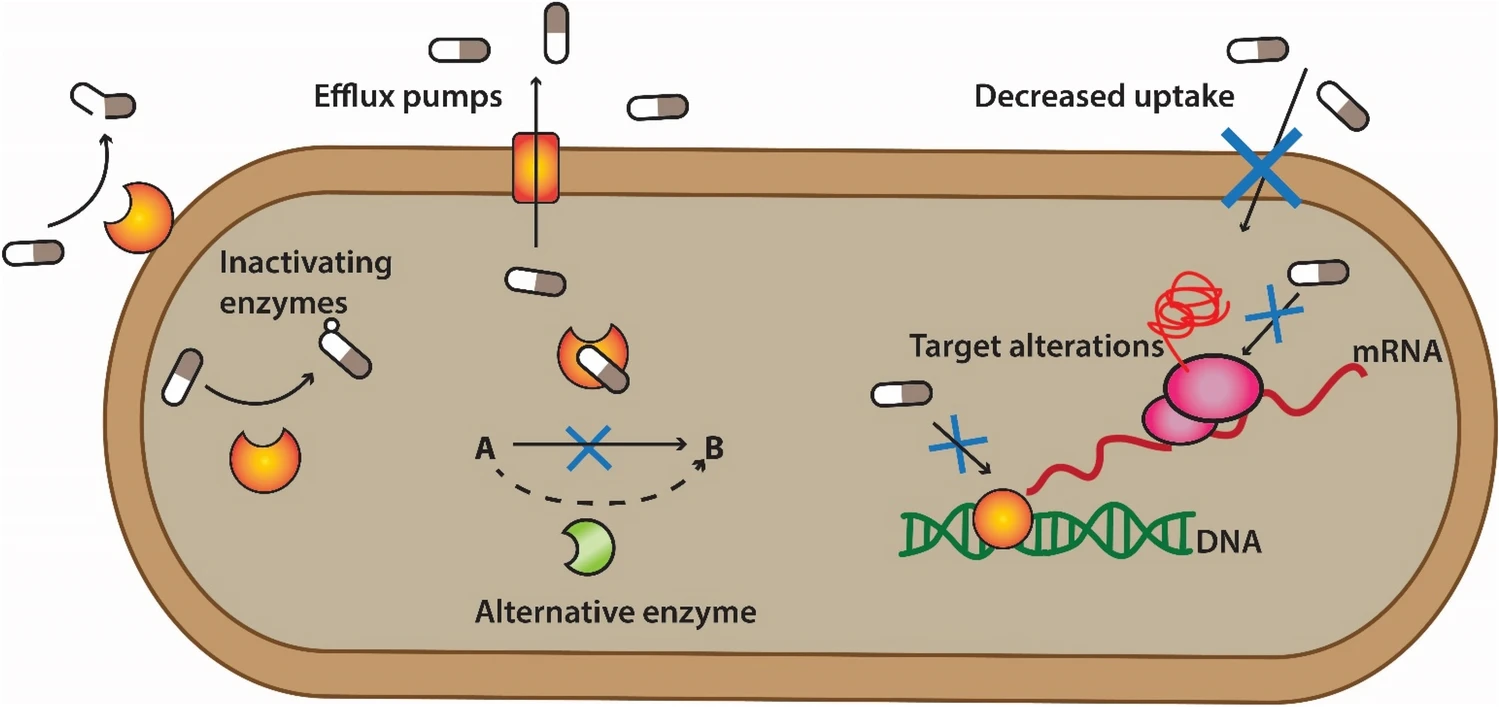 Fig. 2 The mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in bacteria. (Mutuku C, et al., 2022)
Fig. 2 The mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in bacteria. (Mutuku C, et al., 2022)
Our Services
Our firm appreciates the dire need to focus on antibiotic resistance. Our team of scientists is committed to resist back bacteria using novel approaches and high-end technologies. We want to develop antibiotics that will beat the resisting mechanisms by maintaining the state of the art research, this way the antibiotics will be able to save many people for a long time to come.
Workflow of Antibiotic Development

Target Identification
Our specialized team identifies the targets that could be used to stop bacteria growth or survival using a sophisticated organism approach.
Hit Discovery
Hits are considered to be compounds that display activity towards the target of interest. Interacting molecules or compounds that could potentially inhibit the activity of the target are searched for by through compound library screening, natural products screening, virtual screening and also fragment-based drug discovery.
Hit-to-Lead Transition
All properties such as potency, selectivity, pharmacokinetics and safety are taken into consideration while medicinal chemistry methods are employed and structural modifications are carried out on the hits. Trying to find lead compounds with enhanced potency, selection and other desirable traits is the aim of this stage.
Lead Optimization
This step has to do with further developing the lead compound and polishing its drug-like attributes in a bid to improve its efficiency. As a result, testing and analysis of the pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, toxicology among other properties is conducted in detail for further optimization of the lead compound.
Antimicrobial Activity Screening
The screening of antimicrobial activity comprises in vitro testing of pathogens for the efficacy of lead compounds against microorganisms targeting their growth inhibition or elimination. Such tests comprise MIC, MBC, time–kill assays, among others.
Preclinical Studies
Employing animal models infected with microbes, our researchers perform simulation tests on promising compounds in order to assess their safety, effectiveness and pharmacokinetics.
Applicable Infectious Disease Types
Within our organization, we seek to create new antibiotics against diverse bacterial infections. We aim to progress the field of infectious diseases treatment and management through meaningful contributions.
- Acinetobacter Infection
- Actinomycosis
- Bacillus Cereus Infection
- Bacteroides Infection
- Campylobacteriosis
- Carrion's Disease
- Diphtheria
- Ehrlichiosis
- Gas Gangrene
- Human Monocytic Ehrlichiosis
- Kingella Kingae Infection
- And More
If you are interested in our services, please feel free to contact us for more details and quotation information of related services.
References
- Aranda F L, Rivas B L. Removal of amoxicillin through different methods, emphasizing removal by biopolymers and its derivatives. An overview[J]. Journal of the Chilean Chemical Society, 2022, 67(3): 5643-5655.
- Mutuku C, Gazdag Z, Melegh S. Occurrence of antibiotics and bacterial resistance genes in wastewater: resistance mechanisms and antimicrobial resistance control approaches[J]. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2022, 38(9): 152.
All of our services and products are intended for preclinical research use
only and cannot be used to diagnose, treat or manage patients.


 Fig. 1 Mechanisms of action of some antibiotics. (Aranda F L, Rivas B L., 2022)
Fig. 1 Mechanisms of action of some antibiotics. (Aranda F L, Rivas B L., 2022) Fig. 2 The mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in bacteria. (Mutuku C, et al., 2022)
Fig. 2 The mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in bacteria. (Mutuku C, et al., 2022)

