Myasthenia Gravis
Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disorder of the neuromuscular type that is associated with muscle weakness and fatigue. With our extensive experience and advanced technology, we support all stages of service from program design to drug development for myasthenia gravis.
Overview of Myasthenia Gravis
Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune condition which is characterized as a chronic disorder of skeletal muscle and has weakness of the muscles and fatigue. There is an annual incidence of roughly 8 to 10 cases for every million which includes ptosis, diplopia, bulbar facial weakness, and limb weakness as symptoms.
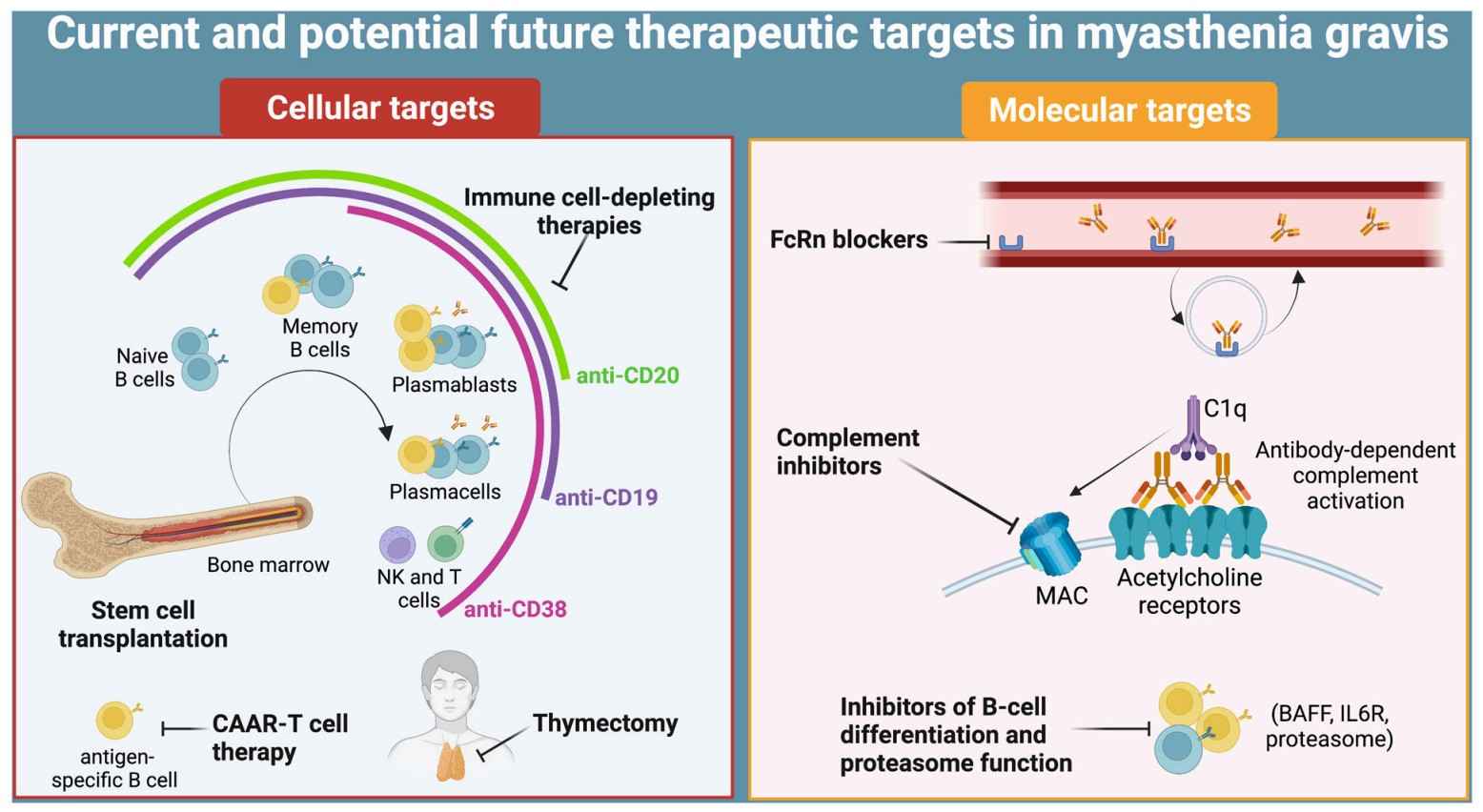 Fig.1 Immunopathogenesis of myasthenia gravis, and therapeutic targets. (Masi, G., and O'Connor, K. C., 2022)
Fig.1 Immunopathogenesis of myasthenia gravis, and therapeutic targets. (Masi, G., and O'Connor, K. C., 2022)Pathogenesis of Myasthenia Gravis
The pathogenesis of this disease is caused by the development of autoantibodies against the acetylcholine nicotinic receptor at the neuromuscular junction which leads to muscle weakness and fatigue. The disease process is defined by an autoimmune pathology that results in loss of neuromuscular transmission. There is an autoimmune attack on certain proteins that ensure proper communication between nerves and muscles.
Diagnostics Development of Myasthenia Gravis
The first step in diagnosing this disease accurately is finding and characterizing particular subtypes of autoantibodies through antibody detection. There have been reports stating that myasthenia gravis can be identified with the help of autoantibodies for various types of diseases.
- Acetylcholine receptor (AChR) antibody
- Muscle-specific kinase (MuSK) antibody
- Agrin antibody
- Lipoprotein-related peptide 4 (LRP4) antibody
- Titin antibody
- Ryanodine receptor antibody
Therapeutics of Myasthenia Gravis
Small Molecule Drug Therapy
Monoclonal Antibody Therapy
Cell Therapy
Our Services
Our company is at the forefront of rare research, offering innovative solutions to improve the lives of individuals affected by myasthenia gravis. We offer animal models and therapeutics development platforms to promote advancements in therapeutic options and understanding of the disease's complexities.
Platforms of Myasthenia Gravis Therapy Development
Animal Models of Myasthenia Gravis
Understanding the pathogenesis of myasthenia gravis and the testing of possible therapy relies heavily on animal models. We developed a comprehensive animal model platform giving scientists access to different myasthenia gravis animal models which will facilitate advanced research.
| Chemical-induced Models | ||
| Chemical induction models involve the administration of specific drugs to interfere with the function of the neuromuscular junction, such as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. | ||
| Optional Models |
|
|
| Genetically Engineered Models | ||
| Genetic engineering models leverage gene editing technologies to introduce mutations associated with myasthenia gravis in experimental animals to mimic the occurrence of disease. | ||
| Optional Models |
|
|
|
||
| Xenotransplantation Models | ||
| Xenotransplantation models involve the transfer of autoantibodies, peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBL), or thymus tissue from myasthenia gravis individuals or other animals with myasthenia gravis to recipient animals. | ||
| Optional Models |
|
|
|
|
|
| Optional Species | Mice, Rats, Sheep, Non-Human Primates, Others | |
We offer all-inclusive services in Myasthenia gravis research, as well as help with pharmacokinetics and biosafety evaluations. If you are interested in our services, please feel free to contact us for more details and quotation information of related services.
References
- Bubuioc, Ana-Maria et al. "The epidemiology of myasthenia gravis." Journal of medicine and life 14.1 (2021): 7-16.
- Masi, Gianvito, and Kevin C O'Connor. "Novel pathophysiological insights in autoimmune myasthenia gravis." Current opinion in neurology 35.5 (2022): 586-596.
- Iorio, Raffaele. "Myasthenia gravis: the changing treatment landscape in the era of molecular therapies." Nature reviews 20.2 (2024): 84-98.
All of our services and products are intended for preclinical research use only and cannot be used to diagnose, treat or manage patients.
