Echinococcosis is a parasitic disease that can be found in both humans and animals. It is caused by the larvae of tapeworms from the Echinococcus genus. Our company is at the forefront of developing novel vaccines and therapeutics for echinococcosis. By leveraging cutting-edge technologies and a deep understanding of the parasite's lifecycle, we aim to deliver innovative solutions to combat this neglected disease.
Overview of Echinococcosis
Echinococcosis is a disease caused by a zoonotic parasitic infection which is acquired from tapeworms of Echinococcus genus such as Echinococcus granulosus, Echinococcus multilocularis. This infection is characterized by the formation of cysts in different organs with the liver and lungs being the most common, causing considerable morbidity and mortality. Echinococcus possesses both definitive hosts, which are usually dogs and intermediate hosts such as sheep, cattle and humans. In humans, the infection can be transmitted through the ingestion of eggs found in contaminated food or directly from infected animals.
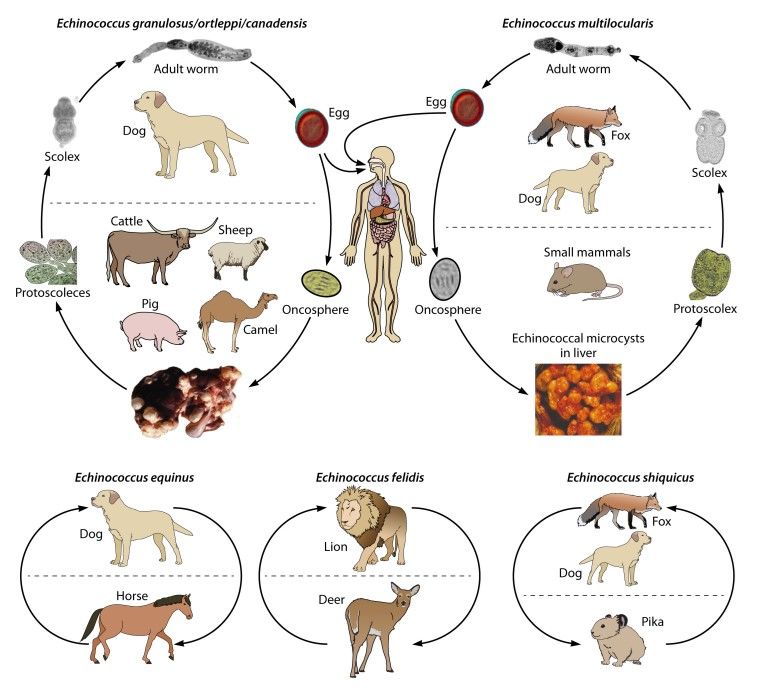 Fig.1 Life cycles of Echinococcus spp. (Wen H., et al., 2019)
Fig.1 Life cycles of Echinococcus spp. (Wen H., et al., 2019)
Vaccine Development for Echinococcosis
Vaccination of Intermediate Hosts: One of the most productive directions in the development of vaccines is targeted at intermediate hosts. These are mainly livestock animals like sheep and goats. The recombinant vaccine EG95 seems to be the foremost candidate as it proved efficacy against CE in sheep.
Vaccination of Definitive Hosts: Vaccination targets are also advanced for definitive hosts such as canids, which are important in the transmission of Echinococcus species. The goal of immunization of definitive hosts is to diminish the shedding of parasite eggs into the environment which is critical to the sustaining cycle of the transmission.
Therapeutics Development for Echinococcosis
- Existing Therapeutics
At present the therapy for echinococcosis is exclusively drug based, and the mainstay pharmacological therapy is the group of medicines known as benzimidazole derivatives, of which albendazole is the drug most used. The primary action of albendazole is parasitostatic. It also prevents the uptake of glucose and the formation of the microtubules in the parasite. Though parasites respond favourably, there are cases of ineffectiveness. There are limits to the use of this drug, such as low availability within the body and the possibility of drug resistance occurring with prolonged use.
Mebendazole, while another benzimidazole with therapeutic applications, is much less efficient than the former Drug. Both of these drugs require to be used for an extended period of time. This in turn can also have a plethora of side effects like liver damage and leukocyte reduction.
- Novel Therapeutic Approaches
There is room for improvement with existing therapies and so harnessing new therapeutics is of utmost relevance. More recently, efforts have been made in drug repurposing by using approved drugs for the treatment of echinococcosis parasitic infection. Such is the case for mefloquine, a drug used for treating malaria that has been effective in reducing parasite load in preclinical trials. The same can be said for nitazoxanide, an antivirulent protozoal medicine that has potential in stunting Echinococcus growth.
Further studies are being conducted on specific Echinococcus pathways using protease inhibitors like bortezomib and the tyrosine kinase sorafenib and imatinib due to their selective targeting which would produce favorable results.
Table 1. Recent advances in drugs for hepatic echinococcosis. (Xu X., et al., 2022)
| Country or territory |
Drug type |
In vivo |
In vitro |
Anticancer ingredient |
| Switzerland |
Antibiotic |
|
ü |
Mefloquine |
| China |
Antibiotic |
ü |
ü |
Nitazoxanide |
| Germany |
Antibiotic |
|
ü |
Amphotericin B |
| Switzerland |
Proteasome inhibitor |
ü |
|
BTZ |
| China |
Multikinase inhibitor |
|
ü |
Sorafenib |
| Germany |
PTKI |
|
ü |
Imatinib |
| Switzerland |
PD-1 inhibitor |
ü |
ü |
PD-1 inhibitor |
| China |
TIGIT inhibitor |
ü |
ü |
TIGIT inhibitor |
Our Services
We are identifying new drug targets and vaccine antigens by conducting genomic studies of various Echinococcus species. Genomic data also sheds light on the biology of the parasite which facilitates the development of more effective intervention strategies. With our outstanding scientists and advanced technology, our firm offers dependable services for the development of echinococcosis vaccines and therapeutics to pharmaceutical companies all over the world.
- Cystic Echinococcosis Rodent Models
- Cystic Echinococcosis Mongolian Gerbil Models
- E. Multilocularis Oral Infection Vole Models
- Secondary Alveolar Echinococcosis Cotton Rat Models
Our bioinformatics team processes and analyzes vast datasets generated from our research, identifying patterns and correlations that inform our drug and vaccine development strategies. If you are interested in our services, please feel free to contact us.
References
- Wen Hao, et al. "Echinococcosis: advances in the 21st century." Clinical microbiology reviews 32.2 (2019): 10-1128.
- Xu, Xiaolei, et al. "Advances in the pharmacological treatment of hepatic alveolar echinococcosis: From laboratory to clinic." Frontiers in microbiology 13 (2022): 953846.
All of our services and products are intended for preclinical research use
only and cannot be used to diagnose, treat or manage patients.


 Fig.1 Life cycles of Echinococcus spp. (Wen H., et al., 2019)
Fig.1 Life cycles of Echinococcus spp. (Wen H., et al., 2019)



